ultralytics 8.0.108 add Meituan YOLOv6 models (#2811)
Co-authored-by: Michael Currie <mcurrie@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Hicham Talaoubrid <98521878+HichTala@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Zlobin Vladimir <vladimir.zlobin@intel.com> Co-authored-by: Szymon Mikler <sjmikler@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
|
|||||||
model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=3) # train the model
|
model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=3) # train the model
|
||||||
metrics = model.val() # evaluate model performance on the validation set
|
metrics = model.val() # evaluate model performance on the validation set
|
||||||
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict on an image
|
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict on an image
|
||||||
success = model.export(format="onnx") # export the model to ONNX format
|
path = model.export(format="onnx") # export the model to ONNX format
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases). See YOLOv8 [Python Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/usage/python) for more examples.
|
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases). See YOLOv8 [Python Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/usage/python) for more examples.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ ADD https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/yolov8n.pt /u
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
# Install pip packages
|
# Install pip packages
|
||||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel
|
RUN python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel
|
||||||
RUN pip install --no-cache -e . albumentations comet tensorboard thop
|
RUN pip install --no-cache -e . albumentations comet tensorboard thop pycocotools
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Set environment variables
|
# Set environment variables
|
||||||
ENV OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
|
ENV OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ In this documentation, we provide information on four major models:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
1. [YOLOv3](./yolov3.md): The third iteration of the YOLO model family, known for its efficient real-time object detection capabilities.
|
1. [YOLOv3](./yolov3.md): The third iteration of the YOLO model family, known for its efficient real-time object detection capabilities.
|
||||||
2. [YOLOv5](./yolov5.md): An improved version of the YOLO architecture, offering better performance and speed tradeoffs compared to previous versions.
|
2. [YOLOv5](./yolov5.md): An improved version of the YOLO architecture, offering better performance and speed tradeoffs compared to previous versions.
|
||||||
|
3. [YOLOv6](./yolov6.md): Released by [Meituan](https://about.meituan.com/) in 2022 and is in use in many of the company's autonomous delivery robots.
|
||||||
3. [YOLOv8](./yolov8.md): The latest version of the YOLO family, featuring enhanced capabilities such as instance segmentation, pose/keypoints estimation, and classification.
|
3. [YOLOv8](./yolov8.md): The latest version of the YOLO family, featuring enhanced capabilities such as instance segmentation, pose/keypoints estimation, and classification.
|
||||||
4. [Segment Anything Model (SAM)](./sam.md): Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM).
|
4. [Segment Anything Model (SAM)](./sam.md): Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM).
|
||||||
5. [Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md): Baidu's RT-DETR model.
|
5. [Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md): Baidu's RT-DETR model.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ For more information about the Segment Anything Model and the SA-1B dataset, ple
|
|||||||
SAM can be used for a variety of downstream tasks involving object and image distributions beyond its training data. Examples include edge detection, object proposal generation, instance segmentation, and preliminary text-to-mask prediction. By employing prompt engineering, SAM can adapt to new tasks and data distributions in a zero-shot manner, making it a versatile and powerful tool for image segmentation tasks.
|
SAM can be used for a variety of downstream tasks involving object and image distributions beyond its training data. Examples include edge detection, object proposal generation, instance segmentation, and preliminary text-to-mask prediction. By employing prompt engineering, SAM can adapt to new tasks and data distributions in a zero-shot manner, making it a versatile and powerful tool for image segmentation tasks.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
```python
|
||||||
from ultralytics.vit import SAM
|
from ultralytics import SAM
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
|
model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
|
||||||
model.info() # display model information
|
model.info() # display model information
|
||||||
|
|||||||
81
docs/models/yolov6.md
Normal file
81
docs/models/yolov6.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
|||||||
|
---
|
||||||
|
comments: true
|
||||||
|
description: Discover Meituan YOLOv6, a robust real-time object detector. Learn how to utilize pre-trained models with Ultralytics Python API for a variety of tasks.
|
||||||
|
---
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Meituan YOLOv6
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Overview
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[Meituan](https://about.meituan.com/) YOLOv6 is a cutting-edge object detector that offers remarkable balance between speed and accuracy, making it a popular choice for real-time applications. This model introduces several notable enhancements on its architecture and training scheme, including the implementation of a Bi-directional Concatenation (BiC) module, an anchor-aided training (AAT) strategy, and an improved backbone and neck design for state-of-the-art accuracy on the COCO dataset.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
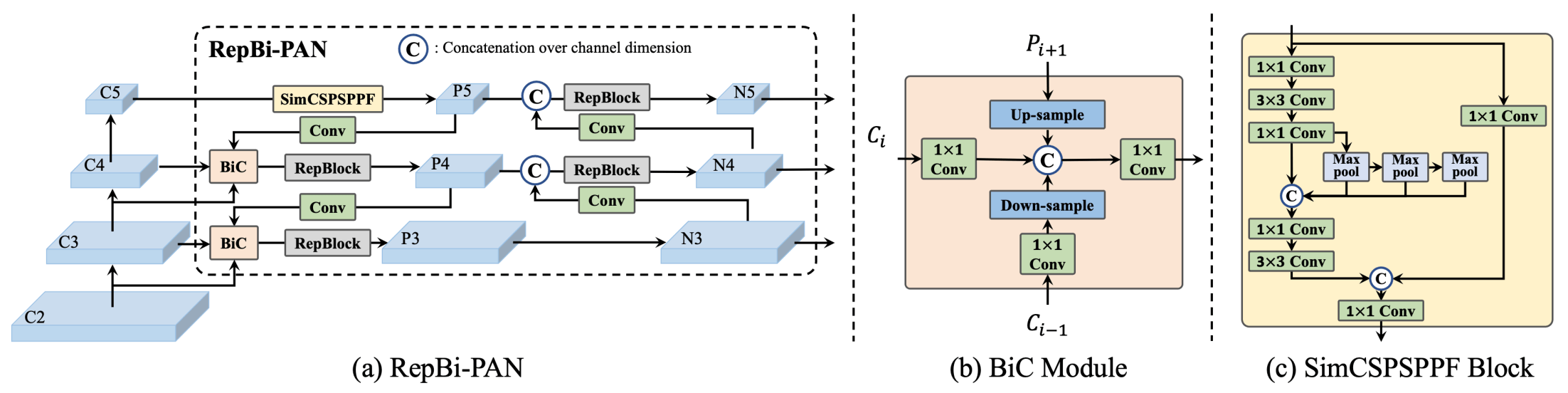
|
||||||
|
**Overview of YOLOv6.** Model architecture diagram showing the redesigned network components and training strategies that have led to significant performance improvements. (a) The neck of YOLOv6 (N and S are shown). Note for M/L, RepBlocks is replaced with CSPStackRep. (b) The
|
||||||
|
structure of a BiC module. (c) A SimCSPSPPF block. ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05586.pdf)).
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Key Features
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **Bi-directional Concatenation (BiC) Module:** YOLOv6 introduces a BiC module in the neck of the detector, enhancing localization signals and delivering performance gains with negligible speed degradation.
|
||||||
|
- **Anchor-Aided Training (AAT) Strategy:** This model proposes AAT to enjoy the benefits of both anchor-based and anchor-free paradigms without compromising inference efficiency.
|
||||||
|
- **Enhanced Backbone and Neck Design:** By deepening YOLOv6 to include another stage in the backbone and neck, this model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the COCO dataset at high-resolution input.
|
||||||
|
- **Self-Distillation Strategy:** A new self-distillation strategy is implemented to boost the performance of smaller models of YOLOv6, enhancing the auxiliary regression branch during training and removing it at inference to avoid a marked speed decline.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Pre-trained Models
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
YOLOv6 provides various pre-trained models with different scales:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- YOLOv6-N: 37.5% AP on COCO val2017 at 1187 FPS with NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU.
|
||||||
|
- YOLOv6-S: 45.0% AP at 484 FPS.
|
||||||
|
- YOLOv6-M: 50.0% AP at 226 FPS.
|
||||||
|
- YOLOv6-L: 52.8% AP at 116 FPS.
|
||||||
|
- YOLOv6-L6: State-of-the-art accuracy in real-time.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
YOLOv6 also provides quantized models for different precisions and models optimized for mobile platforms.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Python API
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```python
|
||||||
|
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
model = YOLO("yolov6n.yaml") # build new model from scratch
|
||||||
|
model.info() # display model information
|
||||||
|
model.predict("path/to/image.jpg") # predict
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Supported Tasks
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported |
|
||||||
|
|------------|---------------------|------------------|
|
||||||
|
| YOLOv6-N | `yolov6-n.pt` | Object Detection |
|
||||||
|
| YOLOv6-S | `yolov6-s.pt` | Object Detection |
|
||||||
|
| YOLOv6-M | `yolov6-m.pt` | Object Detection |
|
||||||
|
| YOLOv6-L | `yolov6-l.pt` | Object Detection |
|
||||||
|
| YOLOv6-L6 | `yolov6-l6.pt` | Object Detection |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Supported Modes
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
| Mode | Supported |
|
||||||
|
|------------|--------------------|
|
||||||
|
| Inference | :heavy_check_mark: |
|
||||||
|
| Validation | :heavy_check_mark: |
|
||||||
|
| Training | :heavy_check_mark: |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Citations and Acknowledgements
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We would like to acknowledge the authors for their significant contributions in the field of real-time object detection:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```bibtex
|
||||||
|
@misc{li2023yolov6,
|
||||||
|
title={YOLOv6 v3.0: A Full-Scale Reloading},
|
||||||
|
author={Chuyi Li and Lulu Li and Yifei Geng and Hongliang Jiang and Meng Cheng and Bo Zhang and Zaidan Ke and Xiaoming Xu and Xiangxiang Chu},
|
||||||
|
year={2023},
|
||||||
|
eprint={2301.05586},
|
||||||
|
archivePrefix={arXiv},
|
||||||
|
primaryClass={cs.CV}
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The original YOLOv6 paper can be found on [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05586). The authors have made their work publicly available, and the codebase can be accessed on [GitHub](https://github.com/meituan/YOLOv6). We appreciate their efforts in advancing the field and making their work accessible to the broader community.
|
||||||
@ -50,14 +50,14 @@ To install the required packages, run:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
The `tune()` method in YOLOv8 provides an easy-to-use interface for hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune. It accepts several arguments that allow you to customize the tuning process. Below is a detailed explanation of each parameter:
|
The `tune()` method in YOLOv8 provides an easy-to-use interface for hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune. It accepts several arguments that allow you to customize the tuning process. Below is a detailed explanation of each parameter:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default Value |
|
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default Value |
|
||||||
|-----------------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|
|
|-----------------|----------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|
|
||||||
| `data` | str | The dataset configuration file (in YAML format) to run the tuner on. This file should specify the training and validation data paths, as well as other dataset-specific settings. | |
|
| `data` | str | The dataset configuration file (in YAML format) to run the tuner on. This file should specify the training and validation data paths, as well as other dataset-specific settings. | |
|
||||||
| `space` | dict, optional | A dictionary defining the hyperparameter search space for Ray Tune. Each key corresponds to a hyperparameter name, and the value specifies the range of values to explore during tuning. If not provided, YOLOv8 uses a default search space with various hyperparameters. | |
|
| `space` | dict, optional | A dictionary defining the hyperparameter search space for Ray Tune. Each key corresponds to a hyperparameter name, and the value specifies the range of values to explore during tuning. If not provided, YOLOv8 uses a default search space with various hyperparameters. | |
|
||||||
| `grace_period` | int, optional | The grace period in epochs for the [ASHA scheduler](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api_docs/schedulers.html#asha-tune-schedulers-asha) in Ray Tune. The scheduler will not terminate any trial before this number of epochs, allowing the model to have some minimum training before making a decision on early stopping. | 10 |
|
| `grace_period` | int, optional | The grace period in epochs for the [ASHA scheduler]https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api/schedulers.html) in Ray Tune. The scheduler will not terminate any trial before this number of epochs, allowing the model to have some minimum training before making a decision on early stopping. | 10 |
|
||||||
| `gpu_per_trial` | int, optional | The number of GPUs to allocate per trial during tuning. This helps manage GPU usage, particularly in multi-GPU environments. If not provided, the tuner will use all available GPUs. | None |
|
| `gpu_per_trial` | int, optional | The number of GPUs to allocate per trial during tuning. This helps manage GPU usage, particularly in multi-GPU environments. If not provided, the tuner will use all available GPUs. | None |
|
||||||
| `max_samples` | int, optional | The maximum number of trials to run during tuning. This parameter helps control the total number of hyperparameter combinations tested, ensuring the tuning process does not run indefinitely. | 10 |
|
| `max_samples` | int, optional | The maximum number of trials to run during tuning. This parameter helps control the total number of hyperparameter combinations tested, ensuring the tuning process does not run indefinitely. | 10 |
|
||||||
| `train_args` | dict, optional | A dictionary of additional arguments to pass to the `train()` method during tuning. These arguments can include settings like the number of training epochs, batch size, and other training-specific configurations. | {} |
|
| `train_args` | dict, optional | A dictionary of additional arguments to pass to the `train()` method during tuning. These arguments can include settings like the number of training epochs, batch size, and other training-specific configurations. | {} |
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
By customizing these parameters, you can fine-tune the hyperparameter optimization process to suit your specific needs and available computational resources.
|
By customizing these parameters, you can fine-tune the hyperparameter optimization process to suit your specific needs and available computational resources.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -163,6 +163,7 @@ nav:
|
|||||||
- models/index.md
|
- models/index.md
|
||||||
- YOLOv3: models/yolov3.md
|
- YOLOv3: models/yolov3.md
|
||||||
- YOLOv5: models/yolov5.md
|
- YOLOv5: models/yolov5.md
|
||||||
|
- YOLOv6: models/yolov6.md
|
||||||
- YOLOv8: models/yolov8.md
|
- YOLOv8: models/yolov8.md
|
||||||
- SAM (Segment Anything Model): models/sam.md
|
- SAM (Segment Anything Model): models/sam.md
|
||||||
- RT-DETR (Realtime Detection Transformer): models/rtdetr.md
|
- RT-DETR (Realtime Detection Transformer): models/rtdetr.md
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|||||||
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
|
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
__version__ = '8.0.107'
|
__version__ = '8.0.108'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from ultralytics.hub import start
|
from ultralytics.hub import start
|
||||||
from ultralytics.vit.rtdetr import RTDETR
|
from ultralytics.vit.rtdetr import RTDETR
|
||||||
|
|||||||
51
ultralytics/models/v6/yolov6.yaml
Normal file
51
ultralytics/models/v6/yolov6.yaml
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
|||||||
|
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv6 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Parameters
|
||||||
|
act: nn.ReLU()
|
||||||
|
nc: 80 # number of classes
|
||||||
|
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov6n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
|
||||||
|
# [depth, width, max_channels]
|
||||||
|
n: [ 0.33, 0.25, 1024 ]
|
||||||
|
s: [ 0.33, 0.50, 1024 ]
|
||||||
|
m: [ 0.67, 0.75, 768 ]
|
||||||
|
l: [ 1.00, 1.00, 512 ]
|
||||||
|
x: [ 1.00, 1.25, 512 ]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv6-3.0s backbone
|
||||||
|
backbone:
|
||||||
|
# [from, repeats, module, args]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 64, 3, 2 ] ] # 0-P1/2
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 128, 3, 2 ] ] # 1-P2/4
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 6, Conv, [ 128, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 256, 3, 2 ] ] # 3-P3/8
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 12, Conv, [ 256, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 512, 3, 2 ] ] # 5-P4/16
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 18, Conv, [ 512, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 1024, 3, 2 ] ] # 7-P5/32
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 9, Conv, [ 1024, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, SPPF, [ 1024, 5 ] ] # 9
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# YOLOv6-3.0s head
|
||||||
|
head:
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, nn.ConvTranspose2d, [ 256, 2, 2, 0 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ [ -1, 6 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ] # cat backbone P4
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 256, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 9, Conv, [ 256, 3, 1 ] ] # 13
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, nn.ConvTranspose2d, [ 128, 2, 2, 0 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ [ -1, 4 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ] # cat backbone P3
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 128, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 9, Conv, [ 128, 3, 1 ] ] # 17
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 128, 3, 2 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ [ -1, 12 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ] # cat head P4
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 256, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 9, Conv, [ 256, 3, 1 ] ] # 21
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 256, 3, 2 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ [ -1, 9 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ] # cat head P5
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 512, 3, 1 ] ]
|
||||||
|
- [ -1, 9, Conv, [ 512, 3, 1 ] ] # 25
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- [ [ 17, 21, 25 ], 1, Detect, [ nc ] ] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
|
||||||
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
|
from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
from ...yolo.utils.torch_utils import model_info
|
||||||
from .build import build_sam
|
from .build import build_sam
|
||||||
from .predict import Predictor
|
from .predict import Predictor
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -33,3 +34,13 @@ class SAM:
|
|||||||
def val(self, **kwargs):
|
def val(self, **kwargs):
|
||||||
"""Run validation given dataset."""
|
"""Run validation given dataset."""
|
||||||
raise NotImplementedError("SAM models don't support validation")
|
raise NotImplementedError("SAM models don't support validation")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def info(self, detailed=False, verbose=True):
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
Logs model info.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Args:
|
||||||
|
detailed (bool): Show detailed information about model.
|
||||||
|
verbose (bool): Controls verbosity.
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
return model_info(self.model, detailed=detailed, verbose=verbose)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -111,10 +111,13 @@ def get_cfg(cfg: Union[str, Path, Dict, SimpleNamespace] = DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, ove
|
|||||||
check_cfg_mismatch(cfg, overrides)
|
check_cfg_mismatch(cfg, overrides)
|
||||||
cfg = {**cfg, **overrides} # merge cfg and overrides dicts (prefer overrides)
|
cfg = {**cfg, **overrides} # merge cfg and overrides dicts (prefer overrides)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Special handling for numeric project/names
|
# Special handling for numeric project/name
|
||||||
for k in 'project', 'name':
|
for k in 'project', 'name':
|
||||||
if k in cfg and isinstance(cfg[k], (int, float)):
|
if k in cfg and isinstance(cfg[k], (int, float)):
|
||||||
cfg[k] = str(cfg[k])
|
cfg[k] = str(cfg[k])
|
||||||
|
if cfg.get('name') == 'model': # assign model to 'name' arg
|
||||||
|
cfg['name'] = cfg.get('model', '').split('.')[0]
|
||||||
|
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ 'name=model' automatically updated to 'name={cfg['name']}'.")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Type and Value checks
|
# Type and Value checks
|
||||||
for k, v in cfg.items():
|
for k, v in cfg.items():
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ def check_source(source):
|
|||||||
is_file = Path(source).suffix[1:] in (IMG_FORMATS + VID_FORMATS)
|
is_file = Path(source).suffix[1:] in (IMG_FORMATS + VID_FORMATS)
|
||||||
is_url = source.lower().startswith(('https://', 'http://', 'rtsp://', 'rtmp://'))
|
is_url = source.lower().startswith(('https://', 'http://', 'rtsp://', 'rtmp://'))
|
||||||
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.streams') or (is_url and not is_file)
|
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.streams') or (is_url and not is_file)
|
||||||
screenshot = source.lower().startswith('screen')
|
screenshot = source.lower() == 'screen'
|
||||||
if is_url and is_file:
|
if is_url and is_file:
|
||||||
source = check_file(source) # download
|
source = check_file(source) # download
|
||||||
elif isinstance(source, tuple(LOADERS)):
|
elif isinstance(source, tuple(LOADERS)):
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -331,12 +331,12 @@ class YOLO:
|
|||||||
overrides = self.overrides.copy()
|
overrides = self.overrides.copy()
|
||||||
overrides.update(kwargs)
|
overrides.update(kwargs)
|
||||||
overrides['mode'] = 'export'
|
overrides['mode'] = 'export'
|
||||||
|
if overrides.get('imgsz') is None:
|
||||||
|
overrides['imgsz'] = self.model.args['imgsz'] # use trained imgsz unless custom value is passed
|
||||||
|
if overrides.get('batch') is None:
|
||||||
|
overrides['batch'] = 1 # default to 1 if not modified
|
||||||
args = get_cfg(cfg=DEFAULT_CFG, overrides=overrides)
|
args = get_cfg(cfg=DEFAULT_CFG, overrides=overrides)
|
||||||
args.task = self.task
|
args.task = self.task
|
||||||
if args.imgsz == DEFAULT_CFG.imgsz:
|
|
||||||
args.imgsz = self.model.args['imgsz'] # use trained imgsz unless custom value is passed
|
|
||||||
if args.batch == DEFAULT_CFG.batch:
|
|
||||||
args.batch = 1 # default to 1 if not modified
|
|
||||||
return Exporter(overrides=args, _callbacks=self.callbacks)(model=self.model)
|
return Exporter(overrides=args, _callbacks=self.callbacks)(model=self.model)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def train(self, **kwargs):
|
def train(self, **kwargs):
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -684,12 +684,17 @@ def check_amp(model):
|
|||||||
im = f if f.exists() else 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' if ONLINE else np.ones((640, 640, 3))
|
im = f if f.exists() else 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' if ONLINE else np.ones((640, 640, 3))
|
||||||
prefix = colorstr('AMP: ')
|
prefix = colorstr('AMP: ')
|
||||||
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}running Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) checks with YOLOv8n...')
|
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}running Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) checks with YOLOv8n...')
|
||||||
|
warning_msg = "Setting 'amp=True'. If you experience zero-mAP or NaN losses you can disable AMP with amp=False."
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||||
assert amp_allclose(YOLO('yolov8n.pt'), im)
|
assert amp_allclose(YOLO('yolov8n.pt'), im)
|
||||||
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}checks passed ✅')
|
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}checks passed ✅')
|
||||||
except ConnectionError:
|
except ConnectionError:
|
||||||
LOGGER.warning(f"{prefix}checks skipped ⚠️, offline and unable to download YOLOv8n. Setting 'amp=True'.")
|
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}checks skipped ⚠️, offline and unable to download YOLOv8n. {warning_msg}')
|
||||||
|
except (AttributeError, ModuleNotFoundError):
|
||||||
|
LOGGER.warning(
|
||||||
|
f'{prefix}checks skipped ⚠️. Unable to load YOLOv8n due to possible Ultralytics package modifications. {warning_msg}'
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
except AssertionError:
|
except AssertionError:
|
||||||
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}checks failed ❌. Anomalies were detected with AMP on your system that may lead to '
|
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix}checks failed ❌. Anomalies were detected with AMP on your system that may lead to '
|
||||||
f'NaN losses or zero-mAP results, so AMP will be disabled during training.')
|
f'NaN losses or zero-mAP results, so AMP will be disabled during training.')
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -372,12 +372,15 @@ def is_online() -> bool:
|
|||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
import socket
|
import socket
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for server in '1.1.1.1', '8.8.8.8', '223.5.5.5': # Cloudflare, Google, AliDNS:
|
for host in '1.1.1.1', '8.8.8.8', '223.5.5.5': # Cloudflare, Google, AliDNS:
|
||||||
try:
|
try:
|
||||||
socket.create_connection((server, 53), timeout=2) # connect to (server, port=53)
|
test_connection = socket.create_connection(address=(host, 53), timeout=2)
|
||||||
return True
|
|
||||||
except (socket.timeout, socket.gaierror, OSError):
|
except (socket.timeout, socket.gaierror, OSError):
|
||||||
continue
|
continue
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
# If the connection was successful, close it to avoid a ResourceWarning
|
||||||
|
test_connection.close()
|
||||||
|
return True
|
||||||
return False
|
return False
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
|||||||
Benchmark a YOLO model formats for speed and accuracy
|
Benchmark a YOLO model formats for speed and accuracy
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Usage:
|
Usage:
|
||||||
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.benchmarks import ProfileModels, run_benchmarks
|
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.benchmarks import ProfileModels, benchmark
|
||||||
ProfileModels(['yolov8n.yaml', 'yolov8s.yaml'])
|
ProfileModels(['yolov8n.yaml', 'yolov8s.yaml'])
|
||||||
run_benchmarks(model='yolov8n.pt', imgsz=160)
|
run_benchmarks(model='yolov8n.pt', imgsz=160)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ class ProfileModels:
|
|||||||
profile(): Profiles the models and prints the result.
|
profile(): Profiles the models and prints the result.
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __init__(self, paths: list, num_timed_runs=100, num_warmup_runs=3, imgsz=640, trt=True):
|
def __init__(self, paths: list, num_timed_runs=100, num_warmup_runs=10, imgsz=640, trt=True):
|
||||||
self.paths = paths
|
self.paths = paths
|
||||||
self.num_timed_runs = num_timed_runs
|
self.num_timed_runs = num_timed_runs
|
||||||
self.num_warmup_runs = num_warmup_runs
|
self.num_warmup_runs = num_warmup_runs
|
||||||
@ -181,22 +181,22 @@ class ProfileModels:
|
|||||||
table_rows = []
|
table_rows = []
|
||||||
device = 0 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
|
device = 0 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
|
||||||
for file in files:
|
for file in files:
|
||||||
engine_file = ''
|
engine_file = file.with_suffix('.engine')
|
||||||
if file.suffix in ('.pt', '.yaml'):
|
if file.suffix in ('.pt', '.yaml'):
|
||||||
model = YOLO(str(file))
|
model = YOLO(str(file))
|
||||||
num_params, num_flops = model.info()
|
model_info = model.info()
|
||||||
if self.trt and device == 0:
|
if self.trt and device == 0 and not engine_file.is_file():
|
||||||
engine_file = model.export(format='engine', half=True, imgsz=self.imgsz, device=device)
|
engine_file = model.export(format='engine', half=True, imgsz=self.imgsz, device=device)
|
||||||
onnx_file = model.export(format='onnx', half=True, imgsz=self.imgsz, simplify=True, device=device)
|
onnx_file = model.export(format='onnx', half=True, imgsz=self.imgsz, simplify=True, device=device)
|
||||||
elif file.suffix == '.onnx':
|
elif file.suffix == '.onnx':
|
||||||
num_params, num_flops = self.get_onnx_model_info(file)
|
model_info = self.get_onnx_model_info(file)
|
||||||
onnx_file = file
|
onnx_file = file
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
continue
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
t_engine = self.profile_tensorrt_model(str(engine_file))
|
t_engine = self.profile_tensorrt_model(str(engine_file))
|
||||||
t_onnx = self.profile_onnx_model(str(onnx_file))
|
t_onnx = self.profile_onnx_model(str(onnx_file))
|
||||||
table_rows.append(self.generate_table_row(file.stem, t_onnx, t_engine, num_params, num_flops))
|
table_rows.append(self.generate_table_row(file.stem, t_onnx, t_engine, model_info))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
self.print_table(table_rows)
|
self.print_table(table_rows)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -216,10 +216,21 @@ class ProfileModels:
|
|||||||
return [Path(file) for file in sorted(files)]
|
return [Path(file) for file in sorted(files)]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_onnx_model_info(self, onnx_file: str):
|
def get_onnx_model_info(self, onnx_file: str):
|
||||||
return 0.0, 0.0
|
# return (num_layers, num_params, num_gradients, num_flops)
|
||||||
|
return 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def iterative_sigma_clipping(self, data, sigma=2, max_iters=5):
|
||||||
|
data = np.array(data)
|
||||||
|
for _ in range(max_iters):
|
||||||
|
mean, std = np.mean(data), np.std(data)
|
||||||
|
clipped_data = data[(data > mean - sigma * std) & (data < mean + sigma * std)]
|
||||||
|
if len(clipped_data) == len(data):
|
||||||
|
break
|
||||||
|
data = clipped_data
|
||||||
|
return data
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def profile_tensorrt_model(self, engine_file: str):
|
def profile_tensorrt_model(self, engine_file: str):
|
||||||
if not Path(engine_file).is_file():
|
if not self.trt or not Path(engine_file).is_file():
|
||||||
return 0.0, 0.0
|
return 0.0, 0.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Warmup runs
|
# Warmup runs
|
||||||
@ -230,10 +241,11 @@ class ProfileModels:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
# Timed runs
|
# Timed runs
|
||||||
run_times = []
|
run_times = []
|
||||||
for _ in tqdm(range(self.num_timed_runs), desc=engine_file):
|
for _ in tqdm(range(self.num_timed_runs * 30), desc=engine_file):
|
||||||
results = model(input_data, verbose=False)
|
results = model(input_data, verbose=False)
|
||||||
run_times.append(results[0].speed['inference']) # Convert to milliseconds
|
run_times.append(results[0].speed['inference']) # Convert to milliseconds
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
run_times = self.iterative_sigma_clipping(np.array(run_times), sigma=2, max_iters=3) # sigma clipping
|
||||||
return np.mean(run_times), np.std(run_times)
|
return np.mean(run_times), np.std(run_times)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def profile_onnx_model(self, onnx_file: str):
|
def profile_onnx_model(self, onnx_file: str):
|
||||||
@ -246,7 +258,23 @@ class ProfileModels:
|
|||||||
sess = ort.InferenceSession(onnx_file, sess_options, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
|
sess = ort.InferenceSession(onnx_file, sess_options, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
input_tensor = sess.get_inputs()[0]
|
input_tensor = sess.get_inputs()[0]
|
||||||
input_data = np.random.rand(*input_tensor.shape).astype(np.float16 if torch.cuda.is_available() else np.float32)
|
input_type = input_tensor.type
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Mapping ONNX datatype to numpy datatype
|
||||||
|
if 'float16' in input_type:
|
||||||
|
input_dtype = np.float16
|
||||||
|
elif 'float' in input_type:
|
||||||
|
input_dtype = np.float32
|
||||||
|
elif 'double' in input_type:
|
||||||
|
input_dtype = np.float64
|
||||||
|
elif 'int64' in input_type:
|
||||||
|
input_dtype = np.int64
|
||||||
|
elif 'int32' in input_type:
|
||||||
|
input_dtype = np.int32
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
raise ValueError(f'Unsupported ONNX datatype {input_type}')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
input_data = np.random.rand(*input_tensor.shape).astype(input_dtype)
|
||||||
input_name = input_tensor.name
|
input_name = input_tensor.name
|
||||||
output_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
|
output_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -261,17 +289,19 @@ class ProfileModels:
|
|||||||
sess.run([output_name], {input_name: input_data})
|
sess.run([output_name], {input_name: input_data})
|
||||||
run_times.append((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) # Convert to milliseconds
|
run_times.append((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) # Convert to milliseconds
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
run_times = self.iterative_sigma_clipping(np.array(run_times), sigma=2, max_iters=3) # sigma clipping
|
||||||
return np.mean(run_times), np.std(run_times)
|
return np.mean(run_times), np.std(run_times)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def generate_table_row(self, model_name, t_onnx, t_engine, num_params, num_flops):
|
def generate_table_row(self, model_name, t_onnx, t_engine, model_info):
|
||||||
return f'| {model_name} | {self.imgsz} | - | {t_onnx[0]:.2f} ± {t_onnx[1]:.2f} ms | {t_engine[0]:.2f} ± {t_engine[1]:.2f} ms | {num_params / 1e6:.1f} | {num_flops:.1f} |'
|
layers, params, gradients, flops = model_info
|
||||||
|
return f'| {model_name:18s} | {self.imgsz} | - | {t_onnx[0]:.2f} ± {t_onnx[1]:.2f} ms | {t_engine[0]:.2f} ± {t_engine[1]:.2f} ms | {params / 1e6:.1f} | {flops:.1f} |'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def print_table(self, table_rows):
|
def print_table(self, table_rows):
|
||||||
gpu = torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'GPU'
|
gpu = torch.cuda.get_device_name(0) if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'GPU'
|
||||||
header = f'| Model | size<br><sup>(pixels) | mAP<sup>val<br>50-95 | Speed<br><sup>CPU ONNX<br>(ms) | Speed<br><sup>{gpu} TensorRT<br>(ms) | params<br><sup>(M) | FLOPs<br><sup>(B) |'
|
header = f'| Model | size<br><sup>(pixels) | mAP<sup>val<br>50-95 | Speed<br><sup>CPU ONNX<br>(ms) | Speed<br><sup>{gpu} TensorRT<br>(ms) | params<br><sup>(M) | FLOPs<br><sup>(B) |'
|
||||||
separator = '|-------------|---------------------|--------------------|------------------------------|-----------------------------------|------------------|-----------------|'
|
separator = '|-------------|---------------------|--------------------|------------------------------|-----------------------------------|------------------|-----------------|'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
print(header)
|
print(f'\n\n{header}')
|
||||||
print(separator)
|
print(separator)
|
||||||
for row in table_rows:
|
for row in table_rows:
|
||||||
print(row)
|
print(row)
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -104,7 +104,8 @@ def scale_boxes(img1_shape, boxes, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
|
|||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
|
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
|
||||||
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
|
gain = min(img1_shape[0] / img0_shape[0], img1_shape[1] / img0_shape[1]) # gain = old / new
|
||||||
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 # wh padding
|
pad = round((img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2 - 0.1), round(
|
||||||
|
(img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2 - 0.1) # wh padding
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
|
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
|
||||||
pad = ratio_pad[1]
|
pad = ratio_pad[1]
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -162,8 +162,9 @@ def model_info(model, detailed=False, verbose=True, imgsz=640):
|
|||||||
"""Model information. imgsz may be int or list, i.e. imgsz=640 or imgsz=[640, 320]."""
|
"""Model information. imgsz may be int or list, i.e. imgsz=640 or imgsz=[640, 320]."""
|
||||||
if not verbose:
|
if not verbose:
|
||||||
return
|
return
|
||||||
n_p = get_num_params(model)
|
n_p = get_num_params(model) # number of parameters
|
||||||
n_g = get_num_gradients(model) # number gradients
|
n_g = get_num_gradients(model) # number of gradients
|
||||||
|
n_l = len(list(model.modules())) # number of layers
|
||||||
if detailed:
|
if detailed:
|
||||||
LOGGER.info(
|
LOGGER.info(
|
||||||
f"{'layer':>5} {'name':>40} {'gradient':>9} {'parameters':>12} {'shape':>20} {'mu':>10} {'sigma':>10}")
|
f"{'layer':>5} {'name':>40} {'gradient':>9} {'parameters':>12} {'shape':>20} {'mu':>10} {'sigma':>10}")
|
||||||
@ -173,11 +174,12 @@ def model_info(model, detailed=False, verbose=True, imgsz=640):
|
|||||||
(i, name, p.requires_grad, p.numel(), list(p.shape), p.mean(), p.std(), p.dtype))
|
(i, name, p.requires_grad, p.numel(), list(p.shape), p.mean(), p.std(), p.dtype))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
flops = get_flops(model, imgsz)
|
flops = get_flops(model, imgsz)
|
||||||
fused = ' (fused)' if model.is_fused() else ''
|
fused = ' (fused)' if getattr(model, 'is_fused', lambda: False)() else ''
|
||||||
fs = f', {flops:.1f} GFLOPs' if flops else ''
|
fs = f', {flops:.1f} GFLOPs' if flops else ''
|
||||||
m = Path(getattr(model, 'yaml_file', '') or model.yaml.get('yaml_file', '')).stem.replace('yolo', 'YOLO') or 'Model'
|
yaml_file = getattr(model, 'yaml_file', '') or getattr(model, 'yaml', {}).get('yaml_file', '')
|
||||||
LOGGER.info(f'{m} summary{fused}: {len(list(model.modules()))} layers, {n_p} parameters, {n_g} gradients{fs}')
|
model_name = Path(yaml_file).stem.replace('yolo', 'YOLO') or 'Model'
|
||||||
return n_p, flops
|
LOGGER.info(f'{model_name} summary{fused}: {n_l} layers, {n_p} parameters, {n_g} gradients{fs}')
|
||||||
|
return n_l, n_p, n_g, flops
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_num_params(model):
|
def get_num_params(model):
|
||||||
@ -199,8 +201,7 @@ def get_flops(model, imgsz=640):
|
|||||||
im = torch.empty((1, p.shape[1], stride, stride), device=p.device) # input image in BCHW format
|
im = torch.empty((1, p.shape[1], stride, stride), device=p.device) # input image in BCHW format
|
||||||
flops = thop.profile(deepcopy(model), inputs=[im], verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # stride GFLOPs
|
flops = thop.profile(deepcopy(model), inputs=[im], verbose=False)[0] / 1E9 * 2 if thop else 0 # stride GFLOPs
|
||||||
imgsz = imgsz if isinstance(imgsz, list) else [imgsz, imgsz] # expand if int/float
|
imgsz = imgsz if isinstance(imgsz, list) else [imgsz, imgsz] # expand if int/float
|
||||||
flops = flops * imgsz[0] / stride * imgsz[1] / stride # 640x640 GFLOPs
|
return flops * imgsz[0] / stride * imgsz[1] / stride # 640x640 GFLOPs
|
||||||
return flops
|
|
||||||
except Exception:
|
except Exception:
|
||||||
return 0
|
return 0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user