ultralytics 8.0.105 classification hyp fix and new onplot callbacks (#2684)
Co-authored-by: ayush chaurasia <ayush.chaurarsia@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Ivan Shcheklein <shcheklein@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
@ -33,9 +33,18 @@ def extract_classes_and_functions(filepath):
|
||||
def create_markdown(py_filepath, module_path, classes, functions):
|
||||
md_filepath = py_filepath.with_suffix('.md')
|
||||
|
||||
# Read existing content and keep header content between first two ---
|
||||
header_content = ""
|
||||
if md_filepath.exists():
|
||||
with open(md_filepath, 'r') as file:
|
||||
existing_content = file.read()
|
||||
header_parts = existing_content.split('---', 2)
|
||||
if len(header_parts) >= 3:
|
||||
header_content = f"{header_parts[0]}---{header_parts[1]}---\n\n"
|
||||
|
||||
md_content = [f"# {class_name}\n---\n:::{module_path}.{class_name}\n<br><br>\n" for class_name in classes]
|
||||
md_content.extend(f"# {func_name}\n---\n:::{module_path}.{func_name}\n<br><br>\n" for func_name in functions)
|
||||
md_content = "\n".join(md_content)
|
||||
md_content = header_content + "\n".join(md_content)
|
||||
|
||||
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(md_filepath), exist_ok=True)
|
||||
with open(md_filepath, 'w') as file:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,81 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Learn about the MNIST dataset, a large database of handwritten digits commonly used for training various image processing systems and machine learning models.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# 🚧 Page Under Construction ⚒
|
||||
# MNIST Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
This page is currently under construction!️ 👷Please check back later for updates. 😃🔜
|
||||
The [MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) (Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology) dataset is a large database of handwritten digits that is commonly used for training various image processing systems and machine learning models. It was created by "re-mixing" the samples from NIST's original datasets and has become a benchmark for evaluating the performance of image classification algorithms.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
- MNIST contains 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images of handwritten digits.
|
||||
- The dataset comprises grayscale images of size 28x28 pixels.
|
||||
- The images are normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel bounding box and anti-aliased, introducing grayscale levels.
|
||||
- MNIST is widely used for training and testing in the field of machine learning, especially for image classification tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset Structure
|
||||
|
||||
The MNIST dataset is split into two subsets:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Training Set**: This subset contains 60,000 images of handwritten digits used for training machine learning models.
|
||||
2. **Testing Set**: This subset consists of 10,000 images used for testing and benchmarking the trained models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Extended MNIST (EMNIST)
|
||||
|
||||
Extended MNIST (EMNIST) is a newer dataset developed and released by NIST to be the successor to MNIST. While MNIST included images only of handwritten digits, EMNIST includes all the images from NIST Special Database 19, which is a large database of handwritten uppercase and lowercase letters as well as digits. The images in EMNIST were converted into the same 28x28 pixel format, by the same process, as were the MNIST images. Accordingly, tools that work with the older, smaller MNIST dataset will likely work unmodified with EMNIST.
|
||||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The MNIST dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's simple and well-structured format makes it an essential resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the MNIST dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 32x32, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a model
|
||||
model = YOLO('yolov8n-cls.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
|
||||
|
||||
# Train the model
|
||||
model.train(data='mnist', epochs=100, imgsz=32)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Start training from a pretrained *.pt model
|
||||
cnn detect train data=MNIST.yaml model=cnn_mnist.pt epochs=100 imgsz=28
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Sample Images and Annotations
|
||||
|
||||
The MNIST dataset contains grayscale images of handwritten digits, providing a well-structured dataset for image classification tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
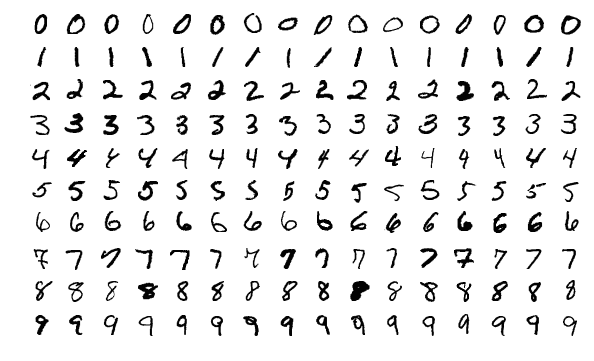
|
||||
|
||||
The example showcases the variety and complexity of the handwritten digits in the MNIST dataset, highlighting the importance of a diverse dataset for training robust image classification models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Citations and Acknowledgments
|
||||
|
||||
If you use the MNIST dataset in your
|
||||
|
||||
research or development work, please cite the following paper:
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@article{lecun2010mnist,
|
||||
title={MNIST handwritten digit database},
|
||||
author={LeCun, Yann and Cortes, Corinna and Burges, CJ},
|
||||
journal={ATT Labs [Online]. Available: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist},
|
||||
volume={2},
|
||||
year={2010}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Yann LeCun, Corinna Cortes, and Christopher J.C. Burges for creating and maintaining the MNIST dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the MNIST dataset and its creators, visit the [MNIST dataset website](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/).
|
||||
@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ Auto-annotation is an essential feature that allows you to generate a segmentati
|
||||
To auto-annotate your dataset using the Ultralytics framework, you can use the `auto_annotate` function as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics.yolo.data import auto_annotate
|
||||
from ultralytics.yolo.data.annotator import auto_annotate
|
||||
|
||||
auto_annotate(data="path/to/images", det_model="yolov8x.pt", sam_model='sam_b.pt')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,6 +9,12 @@ description: Explore RT-DETR, a high-performance real-time object detector. Lear
|
||||
|
||||
Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) is an end-to-end object detector that provides real-time performance while maintaining high accuracy. It efficiently processes multi-scale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion, and supports flexible adjustment of inference speed using different decoder layers without retraining. RT-DETR outperforms many real-time object detectors on accelerated backends like CUDA with TensorRT.
|
||||
|
||||
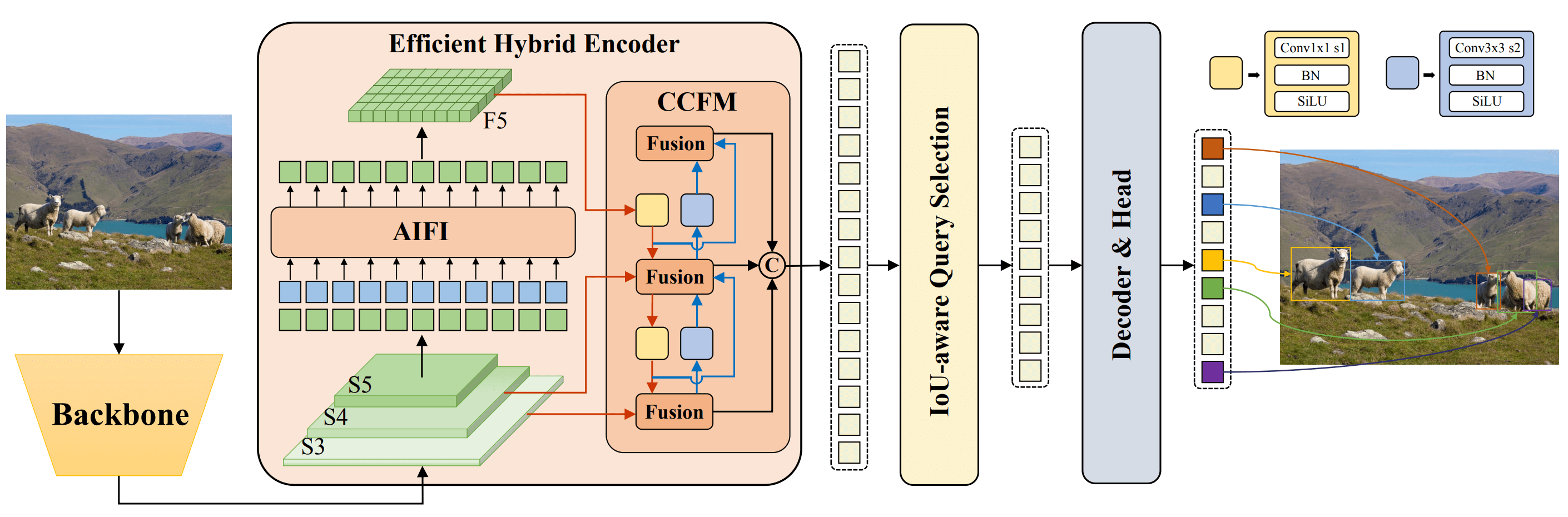
|
||||
**Overview of RT-DETR.** Model architecture diagram showing the last three stages of the backbone {S3, S4, S5} as the input
|
||||
to the encoder. The efficient hybrid encoder transforms multiscale features into a sequence of image features through intrascale feature interaction (AIFI) and cross-scale feature-fusion module (CCFM). The IoU-aware query selection is employed
|
||||
to select a fixed number of image features to serve as initial object queries for the decoder. Finally, the decoder with auxiliary
|
||||
prediction heads iteratively optimizes object queries to generate boxes and confidence scores ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08069.pdf)).
|
||||
|
||||
### Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
- **Efficient Hybrid Encoder:** RT-DETR uses an efficient hybrid encoder that processes multi-scale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. This design reduces computational costs and allows for real-time object detection.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Auto-annotation is an essential feature that allows you to generate a [segmentat
|
||||
To auto-annotate your dataset using the Ultralytics framework, you can use the `auto_annotate` function as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics.yolo.data import auto_annotate
|
||||
from ultralytics.yolo.data.annotator import auto_annotate
|
||||
|
||||
auto_annotate(data="path/to/images", det_model="yolov8x.pt", sam_model='sam_b.pt')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Learn how to use Ultralytics hub authentication in your projects wi
|
||||
# Auth
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.hub.auth.Auth
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Accelerate your AI development with the Ultralytics HUB Training Se
|
||||
# HUBTrainingSession
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.hub.session.HUBTrainingSession
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,4 +20,4 @@ description: Explore Ultralytics events, including 'request_with_credentials' an
|
||||
# smart_request
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.hub.utils.smart_request
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Ensure class names match filenames for easy imports. Use AutoBacken
|
||||
# check_class_names
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.autobackend.check_class_names
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Detect 80+ object categories with bounding box coordinates and clas
|
||||
# Detections
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.autoshape.Detections
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,4 +85,4 @@ description: Explore ultralytics.nn.modules.block to build powerful YOLO object
|
||||
# BottleneckCSP
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.modules.block.BottleneckCSP
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,4 +65,4 @@ description: Explore convolutional neural network modules & techniques such as L
|
||||
# autopad
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.autopad
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,4 +25,4 @@ description: 'Learn about Ultralytics YOLO modules: Segment, Classify, and RTDET
|
||||
# RTDETRDecoder
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.modules.head.RTDETRDecoder
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,4 +50,4 @@ description: Explore the Ultralytics nn modules pages on Transformer and MLP blo
|
||||
# DeformableTransformerDecoder
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.modules.transformer.DeformableTransformerDecoder
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,4 +25,4 @@ description: 'Learn about Ultralytics NN modules: get_clones, linear_init_, and
|
||||
# multi_scale_deformable_attn_pytorch
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.modules.utils.multi_scale_deformable_attn_pytorch
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,4 +65,4 @@ description: Learn how to work with Ultralytics YOLO Detection, Segmentation & C
|
||||
# guess_model_task
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.nn.tasks.guess_model_task
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Learn how to register custom event-tracking and track predictions w
|
||||
# register_tracker
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.track.register_tracker
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: 'TrackState: A comprehensive guide to Ultralytics tracker''s BaseTr
|
||||
# BaseTrack
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.trackers.basetrack.BaseTrack
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: '"Optimize tracking with Ultralytics BOTrack. Easily sort and track
|
||||
# BOTSORT
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.trackers.bot_sort.BOTSORT
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Learn how to track ByteAI model sizes and tips for model optimizati
|
||||
# BYTETracker
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.trackers.byte_tracker.BYTETracker
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: '"Track Google Marketing Campaigns in GMC with Ultralytics Tracker.
|
||||
# GMC
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.utils.gmc.GMC
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Improve object tracking with KalmanFilterXYAH in Ultralytics YOLO -
|
||||
# KalmanFilterXYWH
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.utils.kalman_filter.KalmanFilterXYWH
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,4 +60,4 @@ description: Learn how to match and fuse object detections for accurate target t
|
||||
# bbox_ious
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.tracker.utils.matching.bbox_ious
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Learn how to use auto_annotate in Ultralytics YOLO to generate anno
|
||||
# auto_annotate
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.annotator.auto_annotate
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,4 +90,4 @@ description: Use Ultralytics YOLO Data Augmentation transforms with Base, MixUp,
|
||||
# classify_albumentations
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.augment.classify_albumentations
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Learn about BaseDataset in Ultralytics YOLO, a flexible dataset cla
|
||||
# BaseDataset
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.base.BaseDataset
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,4 +35,4 @@ description: Maximize YOLO performance with Ultralytics' InfiniteDataLoader, see
|
||||
# load_inference_source
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.build.load_inference_source
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ description: Convert COCO-91 to COCO-80 class, RLE to polygon, and merge multi-s
|
||||
# delete_dsstore
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.converter.delete_dsstore
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,4 +35,4 @@ description: 'Ultralytics YOLO Docs: Learn about stream loaders for image and te
|
||||
# autocast_list
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.dataloaders.stream_loaders.autocast_list
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,4 +85,4 @@ description: Enhance image data with Albumentations CenterCrop, normalize, augme
|
||||
# classify_transforms
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.dataloaders.v5augmentations.classify_transforms
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -90,4 +90,4 @@ description: Efficiently load images and labels to models using Ultralytics YOLO
|
||||
# create_classification_dataloader
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.dataloaders.v5loader.create_classification_dataloader
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Create custom YOLOv5 datasets with Ultralytics YOLODataset and Sema
|
||||
# SemanticDataset
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.dataset.SemanticDataset
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Create a custom dataset of mixed and oriented rectangular objects w
|
||||
# MixAndRectDataset
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.dataset_wrappers.MixAndRectDataset
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,4 +65,4 @@ description: Efficiently handle data in YOLO with Ultralytics. Utilize HUBDatase
|
||||
# zip_directory
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.data.utils.zip_directory
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ description: Learn how to export your YOLO model in various formats using Ultral
|
||||
# export
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.engine.exporter.export
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Discover the YOLO model of Ultralytics engine to simplify your obje
|
||||
# YOLO
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.engine.model.YOLO
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: '"The BasePredictor class in Ultralytics YOLO Engine predicts objec
|
||||
# BasePredictor
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.engine.predictor.BasePredictor
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,4 +20,4 @@ description: Learn about BaseTensor & Boxes in Ultralytics YOLO Engine. Check ou
|
||||
# Masks
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.engine.results.Masks
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Train faster with mixed precision. Learn how to use BaseTrainer wit
|
||||
# check_amp
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.engine.trainer.check_amp
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Ensure YOLOv5 models meet constraints and standards with the BaseVa
|
||||
# BaseValidator
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.engine.validator.BaseValidator
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Dynamically adjusts input size to optimize GPU memory usage during
|
||||
# autobatch
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.autobatch.autobatch
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Improve your YOLO's performance and measure its speed. Benchmark ut
|
||||
# benchmark
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.benchmarks.benchmark
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -135,4 +135,4 @@ description: Learn about YOLO's callback functions from on_train_start to add_in
|
||||
# add_integration_callbacks
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.base.add_integration_callbacks
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,4 +35,4 @@ description: Improve your YOLOv5 model training with callbacks from ClearML. Lea
|
||||
# on_train_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.clearml.on_train_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -120,4 +120,4 @@ description: Learn about YOLO callbacks using the Comet.ml platform, enhancing o
|
||||
# on_train_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.comet.on_train_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,4 +40,4 @@ description: Improve YOLOv5 model training with Ultralytics' on-train callbacks.
|
||||
# on_export_start
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.hub.on_export_start
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Track model performance and metrics with MLflow in YOLOv5. Use call
|
||||
# on_train_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.mlflow.on_train_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,4 +40,4 @@ description: Improve YOLOv5 training with Neptune, a powerful logging tool. Trac
|
||||
# on_train_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.neptune.on_train_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: '"Improve YOLO model performance with on_fit_epoch_end callback. Le
|
||||
# on_fit_epoch_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.raytune.on_fit_epoch_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,4 +20,4 @@ description: Learn how to monitor the training process with Tensorboard using Ul
|
||||
# on_fit_epoch_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.tensorboard.on_fit_epoch_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,4 +20,4 @@ description: Learn how to use Ultralytics YOLO's built-in callbacks `on_pretrain
|
||||
# on_train_end
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.callbacks.wb.on_train_end
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,4 +80,4 @@ description: 'Check functions for YOLO utils: image size, version, font, require
|
||||
# print_args
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks.print_args
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,4 +20,4 @@ description: Learn how to find free network port and generate DDP (Distributed D
|
||||
# ddp_cleanup
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.dist.ddp_cleanup
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ description: Download and unzip YOLO pretrained models. Ultralytics YOLO docs ut
|
||||
# download
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.download
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,4 +5,4 @@ description: Learn about HUBModelError in Ultralytics YOLO Docs. Resolve the err
|
||||
# HUBModelError
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.errors.HUBModelError
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,4 +35,4 @@ description: 'Learn about Ultralytics YOLO files and directory utilities: Workin
|
||||
# make_dirs
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.files.make_dirs
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Learn about Bounding Boxes (Bboxes) and _ntuple in Ultralytics YOLO
|
||||
# _ntuple
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.instance._ntuple
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Learn about Varifocal Loss and Keypoint Loss in Ultralytics YOLO fo
|
||||
# KeypointLoss
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.loss.KeypointLoss
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,4 +95,4 @@ description: Explore Ultralytics YOLO's FocalLoss, DetMetrics, PoseMetrics, Clas
|
||||
# ap_per_class
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.metrics.ap_per_class
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -135,4 +135,4 @@ description: Learn about various utility functions in Ultralytics YOLO, includin
|
||||
# clean_str
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.ops.clean_str
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,4 +40,4 @@ description: 'Discover the power of YOLO''s plotting functions: Colors, Labels a
|
||||
# feature_visualization
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.plotting.feature_visualization
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,4 +30,4 @@ description: Improve your YOLO models with Ultralytics' TaskAlignedAssigner, sel
|
||||
# bbox2dist
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.tal.bbox2dist
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -120,4 +120,4 @@ description: Optimize your PyTorch models with Ultralytics YOLO's torch_utils fu
|
||||
# profile
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.utils.torch_utils.profile
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Learn how to use ClassificationPredictor in Ultralytics YOLOv8 for
|
||||
# predict
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.classify.predict.predict
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Train a custom image classification model using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
||||
# train
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.classify.train.train
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Ensure model classification accuracy with Ultralytics YOLO's Classi
|
||||
# val
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.classify.val.val
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Detect and predict objects in images and videos using the Ultralyti
|
||||
# predict
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.detect.predict.predict
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Train and optimize custom object detection models with Ultralytics
|
||||
# train
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.detect.train.train
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Validate YOLOv5 detections using this PyTorch module. Ensure model
|
||||
# val
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.detect.val.val
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Predict human pose coordinates and confidence scores using YOLOv5.
|
||||
# predict
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.pose.predict.predict
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Boost posture detection using PoseTrainer and train models using tr
|
||||
# train
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.pose.train.train
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Ensure proper human poses in images with YOLOv8 Pose Validation, pa
|
||||
# val
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.pose.val.val
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: '"Use SegmentationPredictor in YOLOv8 for efficient object detectio
|
||||
# predict
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.segment.predict.predict
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ description: Learn about SegmentationTrainer and Train in Ultralytics YOLO v8 fo
|
||||
# train
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.segment.train.train
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ description: Ensure segmentation quality on large datasets with SegmentationVali
|
||||
# val
|
||||
---
|
||||
:::ultralytics.yolo.v8.segment.val.val
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
<br><br>
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user