📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5).
UPDATED 26 March 2023.
## Before You Start
Install [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/requirements.txt) in a [**Python>=3.7.0**](https://www.python.org/) environment, including [**PyTorch>=1.7**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). [Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/models) and [datasets](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/data) download automatically from the latest YOLOv5 [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases).
```bash
pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ultralytics/yolov5/master/requirements.txt
```
💡 ProTip: Cloning [https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) is **not** required 😃
## Load YOLOv5 with PyTorch Hub
### Simple Example
This example loads a pretrained YOLOv5s model from PyTorch Hub as `model` and passes an image for inference. `'yolov5s'` is the lightest and fastest YOLOv5 model. For details on all available models please see the [README](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5#pretrained-checkpoints).
```python
import torch
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
# Image
im = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'
# Inference
results = model(im)
results.pandas().xyxy[0]
# xmin ymin xmax ymax confidence class name
# 0 749.50 43.50 1148.0 704.5 0.874023 0 person
# 1 433.50 433.50 517.5 714.5 0.687988 27 tie
# 2 114.75 195.75 1095.0 708.0 0.624512 0 person
# 3 986.00 304.00 1028.0 420.0 0.286865 27 tie
```
### Detailed Example
This example shows **batched inference** with **PIL** and **OpenCV** image sources. `results` can be **printed** to console, **saved** to `runs/hub`, **showed** to screen on supported environments, and returned as **tensors** or **pandas** dataframes.
```python
import cv2
import torch
from PIL import Image
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
# Images
for f in 'zidane.jpg', 'bus.jpg':
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://ultralytics.com/images/' + f, f) # download 2 images
im1 = Image.open('zidane.jpg') # PIL image
im2 = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')[..., ::-1] # OpenCV image (BGR to RGB)
# Inference
results = model([im1, im2], size=640) # batch of images
# Results
results.print()
results.save() # or .show()
results.xyxy[0] # im1 predictions (tensor)
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # im1 predictions (pandas)
# xmin ymin xmax ymax confidence class name
# 0 749.50 43.50 1148.0 704.5 0.874023 0 person
# 1 433.50 433.50 517.5 714.5 0.687988 27 tie
# 2 114.75 195.75 1095.0 708.0 0.624512 0 person
# 3 986.00 304.00 1028.0 420.0 0.286865 27 tie
```
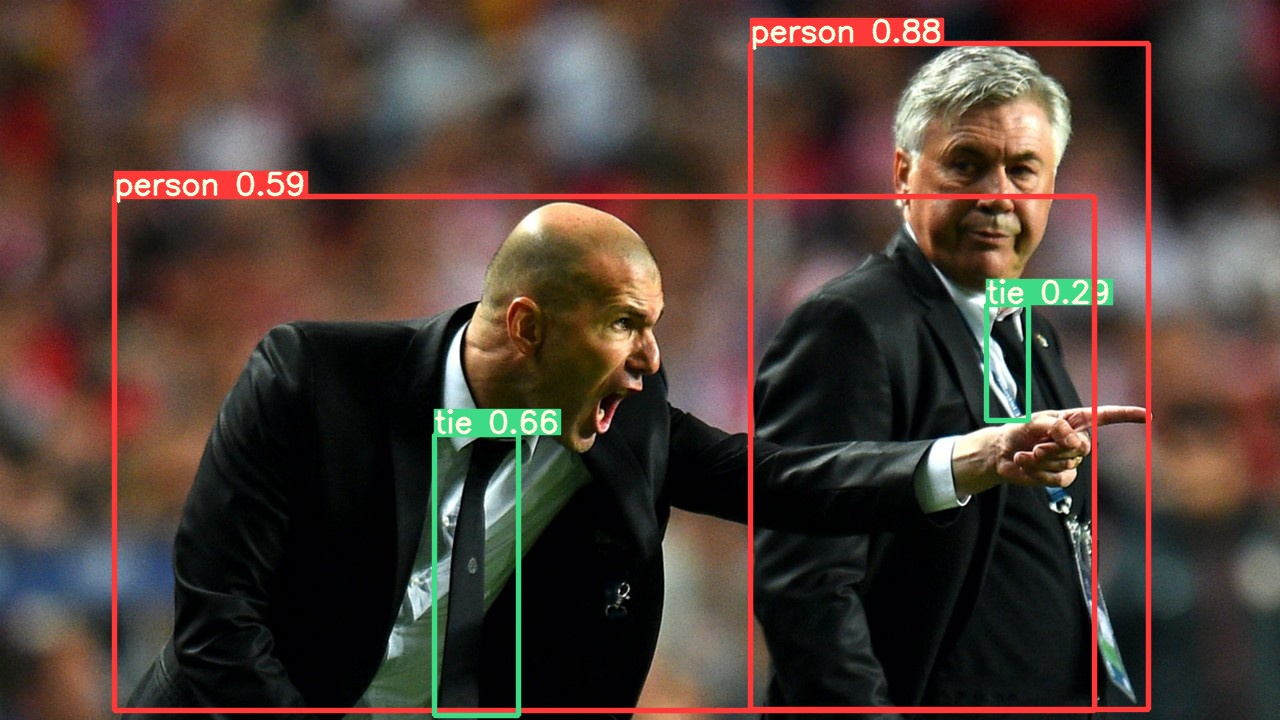
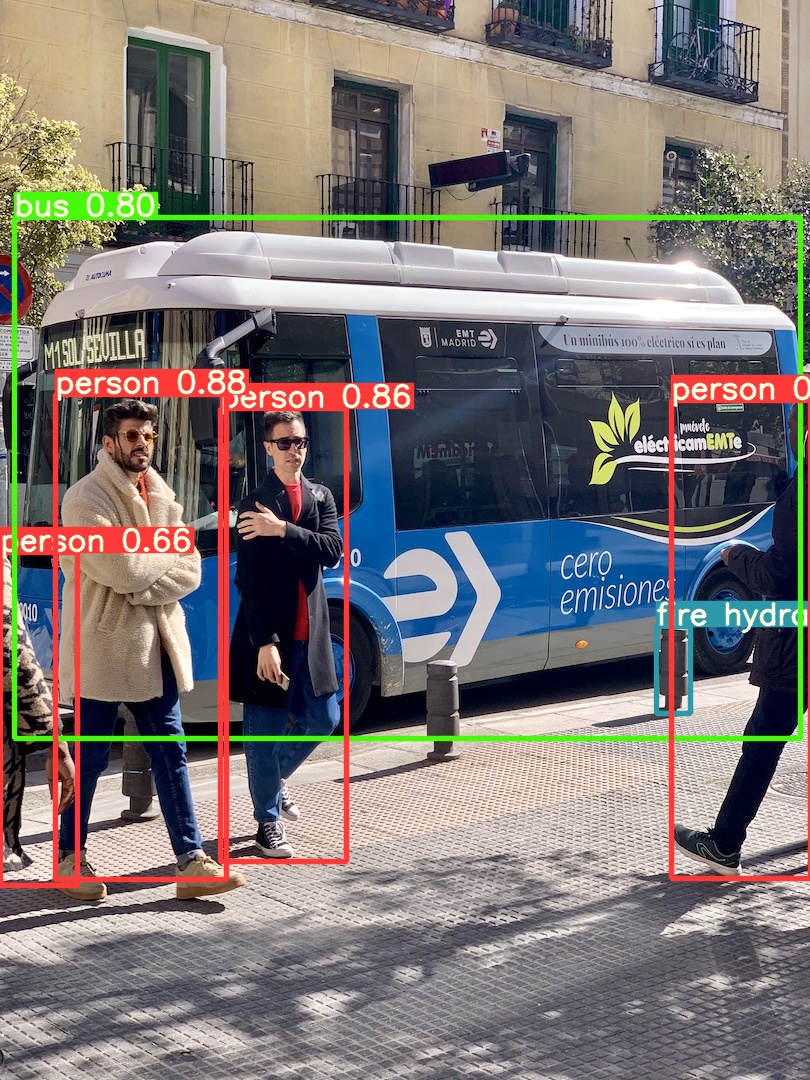 For all inference options see YOLOv5 `AutoShape()` forward [method](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/30e4c4f09297b67afedf8b2bcd851833ddc9dead/models/common.py#L243-L252).
### Inference Settings
YOLOv5 models contain various inference attributes such as **confidence threshold**, **IoU threshold**, etc. which can be set by:
```python
model.conf = 0.25 # NMS confidence threshold
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
results = model(im, size=320) # custom inference size
```
### Device
Models can be transferred to any device after creation:
```python
model.cpu() # CPU
model.cuda() # GPU
model.to(device) # i.e. device=torch.device(0)
```
Models can also be created directly on any `device`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device='cpu') # load on CPU
```
💡 ProTip: Input images are automatically transferred to the correct model device before inference.
### Silence Outputs
Models can be loaded silently with `_verbose=False`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', _verbose=False) # load silently
```
### Input Channels
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 4 input channels rather than the default 3:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', channels=4)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the very first input layer, which is no longer the same shape as the pretrained input layer. The input layer will remain initialized by random weights.
### Number of Classes
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 10 output classes rather than the default 80:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', classes=10)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the output layers, which are no longer the same shape as the pretrained output layers. The output layers will remain initialized by random weights.
### Force Reload
If you run into problems with the above steps, setting `force_reload=True` may help by discarding the existing cache and force a fresh download of the latest YOLOv5 version from PyTorch Hub.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', force_reload=True) # force reload
```
### Screenshot Inference
To run inference on your desktop screen:
```python
import torch
from PIL import ImageGrab
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
# Image
im = ImageGrab.grab() # take a screenshot
# Inference
results = model(im)
```
### Multi-GPU Inference
YOLOv5 models can be loaded to multiple GPUs in parallel with threaded inference:
```python
import torch
import threading
def run(model, im):
results = model(im)
results.save()
# Models
model0 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=0)
model1 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=1)
# Inference
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model0, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model1, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
```
### Training
To load a YOLOv5 model for training rather than inference, set `autoshape=False`. To load a model with randomly initialized weights (to train from scratch) use `pretrained=False`. You must provide your own training script in this case. Alternatively see our YOLOv5 [Train Custom Data Tutorial](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Train-Custom-Data) for model training.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False) # load pretrained
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False, pretrained=False) # load scratch
```
### Base64 Results
For use with API services. See https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2291 and [Flask REST API](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/utils/flask_rest_api) example for details.
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.ims # array of original images (as np array) passed to model for inference
results.render() # updates results.ims with boxes and labels
for im in results.ims:
buffered = BytesIO()
im_base64 = Image.fromarray(im)
im_base64.save(buffered, format="JPEG")
print(base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode('utf-8')) # base64 encoded image with results
```
### Cropped Results
Results can be returned and saved as detection crops:
```python
results = model(im) # inference
crops = results.crop(save=True) # cropped detections dictionary
```
### Pandas Results
Results can be returned as [Pandas DataFrames](https://pandas.pydata.org/):
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # Pandas DataFrame
```
For all inference options see YOLOv5 `AutoShape()` forward [method](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/30e4c4f09297b67afedf8b2bcd851833ddc9dead/models/common.py#L243-L252).
### Inference Settings
YOLOv5 models contain various inference attributes such as **confidence threshold**, **IoU threshold**, etc. which can be set by:
```python
model.conf = 0.25 # NMS confidence threshold
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
results = model(im, size=320) # custom inference size
```
### Device
Models can be transferred to any device after creation:
```python
model.cpu() # CPU
model.cuda() # GPU
model.to(device) # i.e. device=torch.device(0)
```
Models can also be created directly on any `device`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device='cpu') # load on CPU
```
💡 ProTip: Input images are automatically transferred to the correct model device before inference.
### Silence Outputs
Models can be loaded silently with `_verbose=False`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', _verbose=False) # load silently
```
### Input Channels
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 4 input channels rather than the default 3:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', channels=4)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the very first input layer, which is no longer the same shape as the pretrained input layer. The input layer will remain initialized by random weights.
### Number of Classes
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 10 output classes rather than the default 80:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', classes=10)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the output layers, which are no longer the same shape as the pretrained output layers. The output layers will remain initialized by random weights.
### Force Reload
If you run into problems with the above steps, setting `force_reload=True` may help by discarding the existing cache and force a fresh download of the latest YOLOv5 version from PyTorch Hub.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', force_reload=True) # force reload
```
### Screenshot Inference
To run inference on your desktop screen:
```python
import torch
from PIL import ImageGrab
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
# Image
im = ImageGrab.grab() # take a screenshot
# Inference
results = model(im)
```
### Multi-GPU Inference
YOLOv5 models can be loaded to multiple GPUs in parallel with threaded inference:
```python
import torch
import threading
def run(model, im):
results = model(im)
results.save()
# Models
model0 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=0)
model1 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=1)
# Inference
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model0, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model1, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
```
### Training
To load a YOLOv5 model for training rather than inference, set `autoshape=False`. To load a model with randomly initialized weights (to train from scratch) use `pretrained=False`. You must provide your own training script in this case. Alternatively see our YOLOv5 [Train Custom Data Tutorial](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Train-Custom-Data) for model training.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False) # load pretrained
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False, pretrained=False) # load scratch
```
### Base64 Results
For use with API services. See https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2291 and [Flask REST API](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/utils/flask_rest_api) example for details.
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.ims # array of original images (as np array) passed to model for inference
results.render() # updates results.ims with boxes and labels
for im in results.ims:
buffered = BytesIO()
im_base64 = Image.fromarray(im)
im_base64.save(buffered, format="JPEG")
print(base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode('utf-8')) # base64 encoded image with results
```
### Cropped Results
Results can be returned and saved as detection crops:
```python
results = model(im) # inference
crops = results.crop(save=True) # cropped detections dictionary
```
### Pandas Results
Results can be returned as [Pandas DataFrames](https://pandas.pydata.org/):
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # Pandas DataFrame
```
Pandas Output (click to expand)
```python
print(results.pandas().xyxy[0])
# xmin ymin xmax ymax confidence class name
# 0 749.50 43.50 1148.0 704.5 0.874023 0 person
# 1 433.50 433.50 517.5 714.5 0.687988 27 tie
# 2 114.75 195.75 1095.0 708.0 0.624512 0 person
# 3 986.00 304.00 1028.0 420.0 0.286865 27 tie
```
### Sorted Results
Results can be sorted by column, i.e. to sort license plate digit detection left-to-right (x-axis):
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.pandas().xyxy[0].sort_values('xmin') # sorted left-right
```
### Box-Cropped Results
Results can be returned and saved as detection crops:
```python
results = model(im) # inference
crops = results.crop(save=True) # cropped detections dictionary
```
### JSON Results
Results can be returned in JSON format once converted to `.pandas()` dataframes using the `.to_json()` method. The JSON format can be modified using the `orient` argument. See pandas `.to_json()` [documentation](https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/reference/api/pandas.DataFrame.to_json.html) for details.
```python
results = model(ims) # inference
results.pandas().xyxy[0].to_json(orient="records") # JSON img1 predictions
```
JSON Output (click to expand)
```json
[
{"xmin":749.5,"ymin":43.5,"xmax":1148.0,"ymax":704.5,"confidence":0.8740234375,"class":0,"name":"person"},
{"xmin":433.5,"ymin":433.5,"xmax":517.5,"ymax":714.5,"confidence":0.6879882812,"class":27,"name":"tie"},
{"xmin":115.25,"ymin":195.75,"xmax":1096.0,"ymax":708.0,"confidence":0.6254882812,"class":0,"name":"person"},
{"xmin":986.0,"ymin":304.0,"xmax":1028.0,"ymax":420.0,"confidence":0.2873535156,"class":27,"name":"tie"}
]
```
## Custom Models
This example loads a custom 20-class [VOC](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/data/VOC.yaml)-trained YOLOv5s model `'best.pt'` with PyTorch Hub.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='path/to/best.pt') # local model
model = torch.hub.load('path/to/yolov5', 'custom', path='path/to/best.pt', source='local') # local repo
```
## TensorRT, ONNX and OpenVINO Models
PyTorch Hub supports inference on most YOLOv5 export formats, including custom trained models. See [TFLite, ONNX, CoreML, TensorRT Export tutorial](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/251) for details on exporting models.
💡 ProTip: **TensorRT** may be up to 2-5X faster than PyTorch on [**GPU benchmarks**](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963)
💡 ProTip: **ONNX** and **OpenVINO** may be up to 2-3X faster than PyTorch on [**CPU benchmarks**](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613)
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.pt') # PyTorch
'yolov5s.torchscript') # TorchScript
'yolov5s.onnx') # ONNX
'yolov5s_openvino_model/') # OpenVINO
'yolov5s.engine') # TensorRT
'yolov5s.mlmodel') # CoreML (macOS-only)
'yolov5s.tflite') # TFLite
'yolov5s_paddle_model/') # PaddlePaddle
```
## Environments
YOLOv5 may be run in any of the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: 

 - **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/GCP-Quickstart)
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/AWS-Quickstart)
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Docker-Quickstart)
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/GCP-Quickstart)
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/AWS-Quickstart)
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Docker-Quickstart)  ## Status
## Status
 If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
 For all inference options see YOLOv5 `AutoShape()` forward [method](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/30e4c4f09297b67afedf8b2bcd851833ddc9dead/models/common.py#L243-L252).
### Inference Settings
YOLOv5 models contain various inference attributes such as **confidence threshold**, **IoU threshold**, etc. which can be set by:
```python
model.conf = 0.25 # NMS confidence threshold
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
results = model(im, size=320) # custom inference size
```
### Device
Models can be transferred to any device after creation:
```python
model.cpu() # CPU
model.cuda() # GPU
model.to(device) # i.e. device=torch.device(0)
```
Models can also be created directly on any `device`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device='cpu') # load on CPU
```
💡 ProTip: Input images are automatically transferred to the correct model device before inference.
### Silence Outputs
Models can be loaded silently with `_verbose=False`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', _verbose=False) # load silently
```
### Input Channels
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 4 input channels rather than the default 3:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', channels=4)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the very first input layer, which is no longer the same shape as the pretrained input layer. The input layer will remain initialized by random weights.
### Number of Classes
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 10 output classes rather than the default 80:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', classes=10)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the output layers, which are no longer the same shape as the pretrained output layers. The output layers will remain initialized by random weights.
### Force Reload
If you run into problems with the above steps, setting `force_reload=True` may help by discarding the existing cache and force a fresh download of the latest YOLOv5 version from PyTorch Hub.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', force_reload=True) # force reload
```
### Screenshot Inference
To run inference on your desktop screen:
```python
import torch
from PIL import ImageGrab
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
# Image
im = ImageGrab.grab() # take a screenshot
# Inference
results = model(im)
```
### Multi-GPU Inference
YOLOv5 models can be loaded to multiple GPUs in parallel with threaded inference:
```python
import torch
import threading
def run(model, im):
results = model(im)
results.save()
# Models
model0 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=0)
model1 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=1)
# Inference
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model0, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model1, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
```
### Training
To load a YOLOv5 model for training rather than inference, set `autoshape=False`. To load a model with randomly initialized weights (to train from scratch) use `pretrained=False`. You must provide your own training script in this case. Alternatively see our YOLOv5 [Train Custom Data Tutorial](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Train-Custom-Data) for model training.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False) # load pretrained
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False, pretrained=False) # load scratch
```
### Base64 Results
For use with API services. See https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2291 and [Flask REST API](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/utils/flask_rest_api) example for details.
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.ims # array of original images (as np array) passed to model for inference
results.render() # updates results.ims with boxes and labels
for im in results.ims:
buffered = BytesIO()
im_base64 = Image.fromarray(im)
im_base64.save(buffered, format="JPEG")
print(base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode('utf-8')) # base64 encoded image with results
```
### Cropped Results
Results can be returned and saved as detection crops:
```python
results = model(im) # inference
crops = results.crop(save=True) # cropped detections dictionary
```
### Pandas Results
Results can be returned as [Pandas DataFrames](https://pandas.pydata.org/):
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # Pandas DataFrame
```
For all inference options see YOLOv5 `AutoShape()` forward [method](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/30e4c4f09297b67afedf8b2bcd851833ddc9dead/models/common.py#L243-L252).
### Inference Settings
YOLOv5 models contain various inference attributes such as **confidence threshold**, **IoU threshold**, etc. which can be set by:
```python
model.conf = 0.25 # NMS confidence threshold
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
results = model(im, size=320) # custom inference size
```
### Device
Models can be transferred to any device after creation:
```python
model.cpu() # CPU
model.cuda() # GPU
model.to(device) # i.e. device=torch.device(0)
```
Models can also be created directly on any `device`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device='cpu') # load on CPU
```
💡 ProTip: Input images are automatically transferred to the correct model device before inference.
### Silence Outputs
Models can be loaded silently with `_verbose=False`:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', _verbose=False) # load silently
```
### Input Channels
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 4 input channels rather than the default 3:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', channels=4)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the very first input layer, which is no longer the same shape as the pretrained input layer. The input layer will remain initialized by random weights.
### Number of Classes
To load a pretrained YOLOv5s model with 10 output classes rather than the default 80:
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', classes=10)
```
In this case the model will be composed of pretrained weights **except for** the output layers, which are no longer the same shape as the pretrained output layers. The output layers will remain initialized by random weights.
### Force Reload
If you run into problems with the above steps, setting `force_reload=True` may help by discarding the existing cache and force a fresh download of the latest YOLOv5 version from PyTorch Hub.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', force_reload=True) # force reload
```
### Screenshot Inference
To run inference on your desktop screen:
```python
import torch
from PIL import ImageGrab
# Model
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s')
# Image
im = ImageGrab.grab() # take a screenshot
# Inference
results = model(im)
```
### Multi-GPU Inference
YOLOv5 models can be loaded to multiple GPUs in parallel with threaded inference:
```python
import torch
import threading
def run(model, im):
results = model(im)
results.save()
# Models
model0 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=0)
model1 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=1)
# Inference
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model0, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/zidane.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model1, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'], daemon=True).start()
```
### Training
To load a YOLOv5 model for training rather than inference, set `autoshape=False`. To load a model with randomly initialized weights (to train from scratch) use `pretrained=False`. You must provide your own training script in this case. Alternatively see our YOLOv5 [Train Custom Data Tutorial](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Train-Custom-Data) for model training.
```python
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False) # load pretrained
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False, pretrained=False) # load scratch
```
### Base64 Results
For use with API services. See https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2291 and [Flask REST API](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/utils/flask_rest_api) example for details.
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.ims # array of original images (as np array) passed to model for inference
results.render() # updates results.ims with boxes and labels
for im in results.ims:
buffered = BytesIO()
im_base64 = Image.fromarray(im)
im_base64.save(buffered, format="JPEG")
print(base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode('utf-8')) # base64 encoded image with results
```
### Cropped Results
Results can be returned and saved as detection crops:
```python
results = model(im) # inference
crops = results.crop(save=True) # cropped detections dictionary
```
### Pandas Results
Results can be returned as [Pandas DataFrames](https://pandas.pydata.org/):
```python
results = model(im) # inference
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # Pandas DataFrame
```

 - **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/GCP-Quickstart)
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/AWS-Quickstart)
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Docker-Quickstart)
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/GCP-Quickstart)
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/AWS-Quickstart)
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/wiki/Docker-Quickstart)  ## Status
## Status